Climate and environmental protest is being criminalized and repressed around the world. The criminalization of such protests has received a lot of attention in certain countries, including the UK and Australia. But there have not been any attempts to capture the global trend – until now.
We recently published a report, with three University of Bristol colleagues, which shows this repression is indeed a global trend – and that it is becoming more difficult around the world to stand up for climate justice.
This criminalization and repression spans the Global North and South and includes more and less democratic countries. It does, however, take different forms.
Our report distinguishes between climate and environmental protest. The latter are campaigns against specific environmentally destructive projects – most commonly oil and gas extraction and pipelines, deforestation, dam building, and mining. They take place all around the world.
Climate protests are aimed at mitigating climate change by decreasing carbon emissions and tend to make bigger policy or political demands (“cut global emissions now” rather than “don’t build this power plant”). They often take place in urban areas and are more common in the global north.
Four ways to repress activism
The intensifying criminalization and repression is taking four main forms.
1. Anti-protest laws are introduced
Anti-protest laws may give the police more power to stop protests, introduce new criminal offenses, increase sentence lengths for existing offenses, or give policy impunity when harming protesters. In the 14 countries we looked at, we found 22 such pieces of legislation introduced since 2019.
2. Protest is criminalized through prosecution and courts
This can mean using laws against climate and environmental activists that were designed to be used against terrorism or organized crime. In Germany, members of Letzte Generation (Last Generation), a direct action group in the mold of Just Stop Oil, were charged in May 2024 with “forming a criminal organization”. This section of the law is typically used against mafia organizations and has never been applied to a non-violent group.
In the Philippines, anti-terrorism laws have been used against environmentalists who have found themselves unable to return to their home islands. Criminalizing protests can also mean lowering the threshold for prosecution, preventing climate activists from mentioning climate change in court, and changing other court processes to make guilty verdicts more likely. Another example is injunctions that can be taken out by corporations against activists who protest against them.
3. Harsher policing
This stretches from stopping and searching to surveillance, arrests, violence, infiltration, and threatening activists. The policing of activists is carried out not just by state actors like police and armed forces, but also by private actors including private security, organized crime, and corporations.
In Germany, regional police have been accused of collaborating with an energy giant (and its private fire brigade) to evict coal mine protesters, while private security was used extensively in policing anti-mining activists in Peru.
4. Killings and disappearances
Lastly, in the most extreme cases, environmental activists are murdered. This is an extension of the trend for harsher policing, as it typically follows threats by the same range of actors. We used data from the NGO Global Witness to show this is increasingly common in countries including Brazil, the Philippines, Peru, and India. In Brazil, most murders are carried out by organized crime groups while in Peru, it is the police force.
Protests are increasing
To look more closely at the global picture of climate and environmental protest – and the repression of it – we used the Armed Conflicts Location Event database. This showed us that climate protests increased dramatically in 2018-2019 and have not declined since. They make up on average about 4 percent of all protests in the 81 countries that had more than 1,000 protests recorded in the 2012-2023 period:
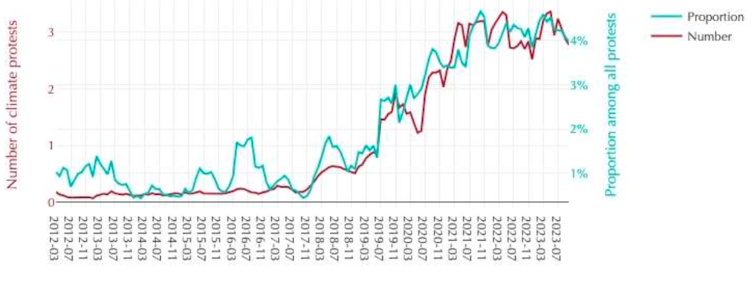
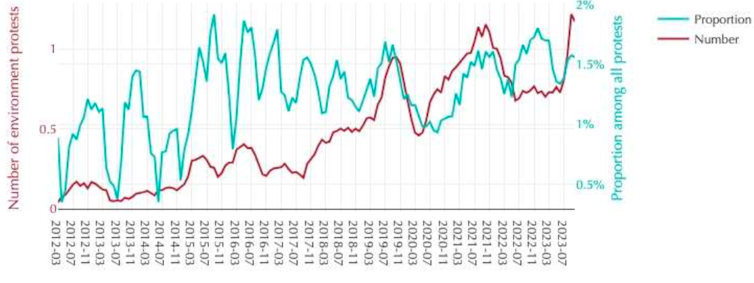
This second graph shows that environmental protest has increased more gradually:
We used this data to see what kind of repression activists face. By looking for keywords in the reporting of protest events, we found that on average 3 percent of climate and environmental protests face police violence, and 6.3 percent involve arrests. But behind these averages are large differences like protest and its policing.
A combination of the presence of protest groups like Extinction Rebellion, who often actively seek arrests, and police forces that are more likely to make arrests, means countries such as Australia and the UK have very high levels of arrest. Some 20 percent of Australian climate and environmental protests involve arrests, against 17 percent in the UK – with the highest in the world being Canada at 27 percent.
Meanwhile, police violence is high in countries such as Peru (6.5 percent) and Uganda (4.4 percent). France stands out as a European country with relatively high levels of police violence (3.2 percent) and low levels of arrests (also 3.2 percent).
In summary, while criminalization and repression do not look the same across the world, there are remarkable similarities. It is increasing in a lot of countries, it involves both state and corporate actors, and it takes many forms.
This repression is taking place in a context where states are not taking adequate action on climate change. By criminalizing activists, states depoliticize them. This conceals the fact these activists are ultimately right about the state of the climate and environment – and the lack of positive government action in these areas.![]() _______________________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Oscar Berglund is a Senior Lecturer in International Public and Social Policy at the University of Bristol, and Tie Franco Brotto is a PhD Candidate at the School for Policy Studies at the University of Bristol.
This article is republished from The Conversation.
